Mechanical Seal Face Materials: Properties and Applications Guide
Meta Description: Learn about mechanical seal face materials like carbon-graphite and SiC. Discover their properties and applications. (99 characters)
Introduction
Why Mechanical Seals Are Vital
Mechanical seals prevent leaks in pumps and fluid-handling systems, ensuring reliable operation. Specifically, the performance of these seals depends on selecting the right seal face materials. For instance, an unsuitable material can cause early failures, whereas the correct choice ensures long-term efficiency.
HongTeng Seals’ Expertise
With over 30 years of expertise at HongTeng Seals, I’ve seen how optimal mechanical seal face materials enhance equipment performance. Therefore, this guide explores common seal face materials, their properties, and their applications to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Seal Face Materials
Key Functions of Seal Faces
Seal face materials form the primary barrier in mechanical seals, containing liquids under tough conditions. To illustrate, they must:
- Stay flat despite varying pressures and temperatures
- Resist wear from constant contact
- Withstand corrosive liquids
- Minimize friction to reduce heat
- Maintain strength to avoid cracking
Factors for Material Selection
However, no single material excels in all areas. Consequently, choosing the right seal face material depends on your application’s needs, such as fluid type, pressure, and environment.
Common Seal Face Materials
Carbon-Graphite: The Go-To Choice
Why Choose Carbon-Graphite?
Carbon-graphite is the most widely used seal face material due to its excellent lubricity, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance. As a result, it suits a variety of applications.
Properties of Carbon-Graphite
- Resin-impregnated: Ideal for water and mild chemicals.
- Metal-impregnated (e.g., antimony): Strong and wear-resistant, perfect for light hydrocarbons (API 682 standard).
- Nickel-impregnated: Corrosion-resistant for oxidizing environments, though harder to source.
Applications for Carbon-Graphite
- Clean water systems
- Light hydrocarbons (e.g., gasoline)
- General chemical processing
- Soft face vs. hard face pairings
Limitations of Carbon-Graphite
- Limited to 1200 PSIG (82 BARG)
- Poor performance in abrasive or high-viscosity fluids (e.g., crude oil)
- Prone to distortion under high pressure
HongTeng’s Carbon-Graphite Solutions
For example, at HongTeng Seals, our engineered carbon-graphite designs improve pressure handling and face contact, enhancing seal performance.
Silicon Carbide: The Durable Ceramic
Why Silicon Carbide Excels
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a robust ceramic, excelling in harsh environments. In particular, its superior wear and chemical resistance make it a top choice for demanding mechanical seal face materials.
Properties of Silicon Carbide
- Reaction-bonded SiC: Offers good thermal conductivity with free silicon.
- Sintered SiC: High-purity, ideal for extreme temperatures and chemicals.
- Graphite-loaded SiC: Provides lubricity for dry-run conditions.
- Porous SiC: Micro-pores enhance cooling and hydrodynamic lift.
Applications for Silicon Carbide
- High-pressure systems
- Abrasive fluids (e.g., slurries)
- High-temperature environments
- Corrosive chemicals
- Thermal shock conditions
Limitations of Silicon Carbide
- Higher cost than carbon-graphite
- Brittle, requiring careful handling
- Needs robust drive designs
- Poor self-compatibility without lubrication
Why SiC Is Worth It
Moreover, SiC’s durability makes it a worthwhile investment for critical applications.
Tungsten Carbide: The Robust Option
Why Use Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide balances hardness and toughness, making it ideal for heavy-duty mechanical seal face materials. As such, it performs well in challenging conditions.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
- Nickel-bound: Corrosion-resistant, common in oil and gas.
- Cobalt-bound: Stronger but less corrosion-resistant.
- Binder levels (6–12%) affect wear and toughness.
Applications for Tungsten Carbide
- High-pressure, shock-loaded systems
- Vibration-heavy environments
- Abrasive media
- Crude oil and viscous fluids
Limitations of Tungsten Carbide
- Lower pressure-velocity (PV) capacity than SiC
- Risk of heat checking
- Heavier and more expensive than carbon
- Binder corrosion in aggressive chemicals
Optimizing Tungsten Carbide
In addition, careful material pairing can mitigate some of these limitations.
Ceramic (Aluminum Oxide): The Cost-Effective Choice
Why Choose Aluminum Oxide?
Aluminum oxide ceramic (99.5% pure) is a cost-effective seal face material for light-duty applications. For instance, its affordability makes it popular in budget-conscious projects.
Properties of Aluminum Oxide
- High hardness and chemical inertness
- Lightweight and electrically insulating
- Affordable
Applications for Aluminum Oxide
- Clean water systems
- Food and beverage processing
- Light-duty chemicals
- Cost-sensitive projects
Limitations of Aluminum Oxide
- Poor thermal shock resistance
- Brittle, prone to damage during installation
- Limited pressure capacity
When to Use Aluminum Oxide
Nevertheless, aluminum oxide is a reliable choice for less demanding environments.
Specialty Materials for Unique Needs
Custom Solutions for Extreme Conditions
In extreme conditions, specialty seal face materials provide tailored solutions. Specifically:
- Silicon Carbide/Graphite Composites: Low friction, ideal for crude oil and high-pressure hydrocarbons.
- Glass-Filled PTFE: High chemical resistance for low-duty corrosive applications.
- Ni-Resist and 17-4 Stainless Steel: Cost-effective for fresh water with thermal cycling.
Benefits of Specialty Materials
Thus, these materials address niche challenges effectively.
Material Pairing for Optimal Performance
Why Pairing Matters
Choosing the right seal face material pairing is crucial for seal performance. To clarify:
- Hard/Soft Pairing: Carbon (soft) vs. ceramic or carbide (hard) works well for clean fluids.
- Hard/Hard Pairing: Best for abrasive or viscous environments.
- Tribology: Carbon vs. SiC offers better heat and friction performance than carbon vs. tungsten.
- Environmental Considerations: Factor in fluid chemistry, temperature, and solids when pairing.
Enhancing Seal Efficiency
For example, proper pairing enhances seal longevity and efficiency.
Application-Specific Recommendations
Tailored Material Choices
Based on HongTeng Seals’ expertise, here are tailored seal face material choices:
- Refined Hydrocarbons:
- Primary: Antimony carbon
- Mating: Reaction-bonded SiC
- Why: High PV rating and compatibility
- Crude Oil:
- Primary: Graphite-loaded or reaction-bonded SiC
- Mating: Sintered SiC or tungsten carbide
- Why: Handles abrasion and viscosity
- Water Services:
- Primary: Resin-impregnated carbon
- Mating: Aluminum oxide or SiC
- Why: Cost-effective for clean fluids
- Chemical Processing:
- Primary: Carbon or SiC
- Mating: Alpha sintered SiC
- Why: Superior chemical resistance
- High-Pressure Services:
- Primary: Engineered carbon or SiC
- Mating: SiC or tungsten carbide
- Why: Prevents distortion under pressure
Maximizing Seal Performance
Therefore, matching materials to applications is key to optimal performance.
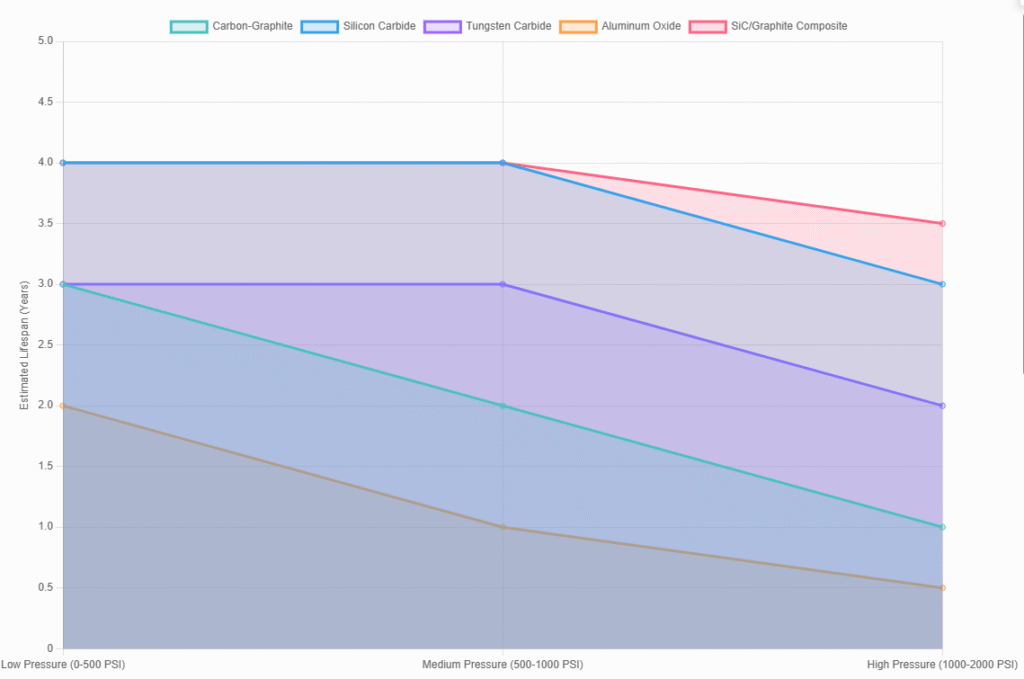
Comparison Table: Seal Face Materials
| Material | Hardness | Chemical Resistance | Cost | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-Graphite | Moderate | Good | Low | Water, hydrocarbons |
| Silicon Carbide | High | Excellent | High | Abrasive, high-pressure |
| Tungsten Carbide | High | Moderate | High | Viscous, shock-loaded |
| Aluminum Oxide | High | Good | Low | Clean water, light-duty |
| SiC/Graphite Composite | High | Excellent | High | Crude oil, high-pressure |

Conclusion
Choosing the Best Seal Face Materials
Selecting the right mechanical seal face materials is essential for equipment reliability and cost efficiency. In particular, understanding your application’s pressure, fluid type, and operating conditions helps you choose materials that maximize performance and minimize downtime. For example, carbon-graphite suits clean fluids, while silicon carbide excels in abrasive conditions.
HongTeng’s Expert Support
Need help selecting the perfect seal face material? Contact HongTeng Seals at for expert guidance tailored to your needs.
